Unlike traditional tools, ArgoCD uses Git repositories to hold the precise definition of your application's desired state, making it your single source of trust.
𝗪𝗵𝗮𝘁 𝗠𝗮𝗸𝗲𝘀 𝗔𝗿𝗴𝗼𝗖𝗗 𝗦𝗽𝗲𝗰𝗶𝗮𝗹?
𝗔𝘂𝘁𝗼𝗺𝗮𝘁𝗲𝗱 𝗗𝗲𝗽𝗹𝗼𝘆𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁𝘀:ArgoCD can automatically deploy your applications to your cluster, be it through a Git commit, a CI/CD pipeline trigger, or even a manual request. Think of the time and effort you'll save!
𝗜𝗻𝘀𝘁𝗮𝗻𝘁 𝗢𝗯𝘀𝗲𝗿𝘃𝗮𝗯𝗶𝗹𝗶𝘁𝘆: With its GUI and CLI, ArgoCD lets developers instantly check whether the application's live state aligns with the desired state. It’s like having a crystal ball for your deployments.
Powerful Operations: It's not just about top-level resources. ArgoCD's UI provides a detailed view of the entire application resource hierarchy, including the underlying ReplicaSets and Pods. Want to see Pod logs and Kubernetes events? It’s all there in a multi-cluster dashboard.
𝗪𝗵𝘆 𝗔𝗿𝗴𝗼𝗖𝗗?
ArgoCD is more than just a tool, it's a strategy in the chaotic world of DevOps. It helps:
✅ Bring order to the chaos
✅ Reach your DevOps milestones
✅ Save precious time and energy for your team
𝗕𝗲 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗩𝗶𝗰𝘁𝗼𝗿 𝗶𝗻 𝗬𝗼𝘂𝗿 𝗗𝗲𝘃𝗢𝗽𝘀 𝗕𝗮𝘁𝘁𝗹𝗲
If your DevOps environment feels overwhelming, ArgoCD might be the tool you've been searching for. It's designed to tame the chaos, streamline operations, and position you as a victor in the ever-challenging DevOps landscape.
Setup ArgoCD in your kubernetes cluster
if you have a cluster not up and running already follow the article here to set up one -
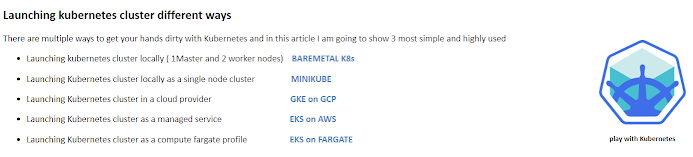 |
| Launch k8s-cluster |
Create argocd namespace in your cluster$ kubectl create namespace argocd
Run the Argo CD install script provided by the project maintainers
$ kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
Verify the argocd pods and resources$ kubectl get all -n argocd $ watch kubectl get pods -n argocd
expose your argocd-server deployment as NP or LB type to access Argo CD$ kubectl expose deploy/argocd-server --type=NodePort --name=arg-svc $ kubectl expose deploy/argocd-server --type=LoadBalancer --name=argcd-svc
Alternatively if you are deploying it to a cloud k8s service, use - $ kubectl patch svc argocd-server -n argocd -p '{"spec": {"type": "LoadBalancer"}}' Fetch the LoadBalancer DNS $ export ARGOCD_SERVER=`kubectl get svc argocd-server -n argocd -o json \ | jq --raw-output '.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname'` $ echo $ARGOCD_SERVER
Fetch the passwd of argocd from secrets $ kubectl get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o yaml $ echo "Q20yMGV0DeMo05WZ0otZg==" | base64 -d Cm20eDeMoSNVgJ-f
OR
$ kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d; echo
$ kubectl patch secret argocd-secret -p '{"data": {"admin.password": null, "admin.passwordMtime": null}}' -n argocd
$ kubectl delete pod/argocd-server-756bbc65c5-zttw4 -n argocd fetch new pass again - $ kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d; echo
✅ create application
✅ Sync up your deployment


